TensorFlow加载CSV数据
本教程提供了有关如何将CSV数据从文件加载到tf.data.Dataset的示例。
本教程中使用的数据取自《泰坦尼克号》乘客列表。该模型将根据年龄,性别,机票等级以及是否独自旅行等特征来预测乘客幸存的可能性。
设定
|
|
加载数据
首先,让我们看一下CSV文件的前几行,以了解其格式。
|
|
你可以使用pandas加载它,并将NumPy数组传递给TensorFlow。如果你需要扩展到一个大的文件集,或者需要一个与TensorFlow和tf.data集成的数据集,请使用tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset函数:
唯一需要明确标识的列是模型要预测的值的列。
|
|
现在,从文件中读取CSV数据并创建一个数据集。(有关完整文档,请参阅tf.data.experimental.make_csv_dataset)
|
|
数据集中的每个项目都是一个批量,表示为(许多示例,许多标签)的元组。示例中的数据以基于列的张量(而不是基于行的张量)进行组织,每个张量具有与批量大小一样多的元素(本例中为5)。
自己看一下也许会有所帮助。
|
|
如你所见,CSV中的列已命名。数据集构造函数将自动获取这些名称。如果使用的文件的第一行不包含列名,则将它们以字符串列表的形式传递给make_csv_dataset函数中的column_names参数。
|
|
本示例将使用所有可用的列。如果你需要从数据集中省略一些列,请创建想要使用的列的列表,并将其传递到构造函数的(可选)select_columns参数中。
|
|
数据预处理
CSV文件可以包含多种数据类型。通常,你需要先将这些混合类型转换为固定长度的向量,然后再将数据输入模型。
TensorFlow有一个用于描述常见输入转换的内置系统:tf.feature_column,请参阅此教程以获取详细信息。
你可以使用任何喜欢的工具(如nltk或sklearn)对数据进行预处理,然后将处理后的输出传递给TensorFlow。
在模型内部进行预处理的主要优点是,当导出模型时,它包括预处理。这样,你可以将原始数据直接传递到模型。
连续数据
如果你的数据已经采用适当的数字格式,则可以将数据打包为向量,然后再传递给模型:
|
|
这是一个将所有列打包在一起的简单函数:
|
|
将此应用于数据集的每个元素:
|
|
如果你有混合数据类型,则可能需要将这些简单数字字段分开。tf.feature_columnapi可以处理它们,但这会产生一些开销,除非确实需要,否则应该避免。切换回混合数据集:
|
|
因此,定义一个更通用的预处理器,该预处理器选择一系列数字特征并将其打包到单个列中:
|
|
数据归一化
连续数据应始终归一化。
|
|
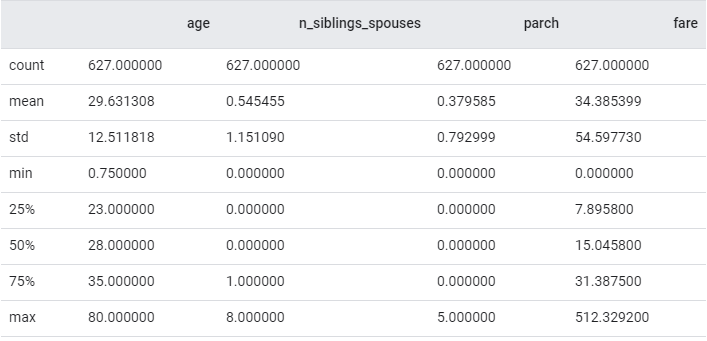
|
|
现在创建一个数值列。tf.feature_columns.numeric_columnAPI接受一个normalizer_fn参数,该参数将在每个批量上运行。
使用functools.partial函数将MEAN和STD绑定到normalizer fn。
|
|
训练模型时,请选择包含此特征列并将此数据块的数值居中:
|
|
这里使用的是基于均值的归一化,要求提前知道每一列的均值。
分类数据
CSV数据中的某些列是分类列。也就是说,内容应该是一组有限的选项之一。
使用tf.feature_columnAPI为每个分类创建一个具有tf.feature_column.indicator_column的集合。
|
|
稍后在构建模型时,这将成为数据处理输入的一部分。
组合预处理层
添加两个特征列集合,并将它们传递给tf.keras.layers.DenseFeatures以创建一个输入层,该层将提取并预处理这两种输入类型:
|
|
建立模型
建立一个以preprocessing_layer开始的tf.keras.Sequential。
|
|
训练、评估和预测
现在可以实例化和训练模型。
|
|
训练模型后,你可以在test_data数据集上测试模型的准确性。
|
|
使用tf.keras.Model.predict预测批量或批量数据集上的标签。
|
|
- 原文作者:百年孤独
- 原文链接:https://qoanty.github.io/2019/10/tensorflow-load-csv-data/
- 版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可,非商业转载请注明出处(作者,原文链接),商业转载请联系作者获得授权。